

Next: Conclusions
Up: Belgian project on humanitarian
Previous: Metal detector expert
The principles of operation of imaging metal detector, GPR and infrared camera, their
complementary information, factors that affect their operability lead to the conclusion that their
fusion should result in improved detectability and reduced number of false alarms in various
situations (different types of mines, of soil, vegetation, moisture, etc.). Therefore, we have
been analyzing possibilities to combine these three sensors, but the model we have been
developing is quite general, i.e. it can be easily modified to include other sensors as well.
Since in this domain of application we have to deal with uncertainty, ambiguity, partial
knowledge and ignorance, we choose an approach where they can be appropriately modelled,
and that is: belief functions within the framework of Dempster-Shafer theory. A main
motivation for working within this framework is to be able to easily model and include existing
knowledge regarding: chosen mine detection sensors, mine laying principles, mines, and
objects that can be confused with mines.
In order to illustrate our approach, let us analyze a very frequent case in reality - detection of
high-metal content objects. Since all three sensors give images, i.e. information about size of
an object, the following four classes create the frame of discernment 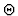 :
:
- MMR (metallic mine of regular shape),
- MMI (metallic mine of irregular shape),
- MFR (metallic friendly, i.e. non-dangerous, object of regular shape),
- MFI (metallic friend of irregular shape).
Furthermore, the criteria that can give the most information about the real
identity of the object in this case, for our knowledge, are the following:
- for each of the three sensors:
- 1.
- ellipse fitting, that is, how well the shape of the object fits in an
ellipse, assigning masses to subsets {MR, FR}, {MI, FI},
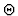 ;
;
- 2.
- shape elongation, again giving masses to {MR, FR}, {MI, FI},
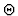 ;
;
- 3.
- area/size, by which information about expectable size range of mines is
included, assigning mass mainly to
 within that range, and to
{FR, FI} elsewhere;
within that range, and to
{FR, FI} elsewhere;
- for MD: burial depth, including the knowledge about the depths where mines
can be expected, so, again, assigning masses to
 and {FR, FI};
and {FR, FI};
- for GPR:
- 1.
- depth dimension of the object, that gives, similarly as information about
area, masses to {FR, FI} and to
 ;
;
- 2.
- comparison of the depth position of metal detected by MD and the object
depth interval sensed by GPR; if they are in accordance, masses are assigned
mainly to
 ,
if they are not, a largest part of masses should go to
subset {FR, FI}.
,
if they are not, a largest part of masses should go to
subset {FR, FI}.
The masses are defined as functions depending on measure of ellipticity,
elongation factor, area, depth, respectively. They are detailed in
[18]; see also example in Figure 1.
Figure 27:
Mass assignments for the area (left) and burial depth (right)
criterion
|
|
After assigning masses for all sensors and all criteria, we combine them using well-known
Dempster's rule in unnormalized form 9in order to preserve potential conflict between
sensors). After that, guesses about the real identity of object under observation are made, on
the basis of the strength of belief assigned to each subclass of the frame of discernment. This
list of guesses is served to a deminer, together with confidence degrees, as well as processed
data of each sensor, in order to help him in making his final decision.


Next: Conclusions
Up: Belgian project on humanitarian
Previous: Metal detector expert
Marc Acheroy
2000-08-03
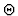 ;
;
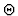 ;
;
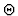 within that range, and to
{FR, FI} elsewhere;
within that range, and to
{FR, FI} elsewhere;
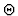 ;
;
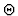 ,
if they are not, a largest part of masses should go to
subset {FR, FI}.
,
if they are not, a largest part of masses should go to
subset {FR, FI}.
![\includegraphics[width=16cm]{fig2.ps}](img57.gif)